A new Construction Service Law No. 2 of 2017 (“New Construction Law”) was enacted in Indonesia on 12 January 2017 which replaces Law No. 18 of 1999 concerning Construction Service (“Law 18/1999”). The New Construction Law is more comprehensive than Law 18/1999 as new provisions are added in order to complement and correspond with existing laws and regulations such as Manpower Law, Information and Electronic Transaction Law, and Regional Authority Law.
The implementing regulation of the New Construction Law has yet to come into force, which shall be enacted no later than 2 years from the issuance of the New Construction Law. Current implementing regulations remain valid so long as they are not inconsistent with the New Construction Law.
9 key changes proposed under the new Construction Law:
1. New types and classifications of construction business services
Law 18/1999:
Previously, Law 18/1999 stipulated 3 types of construction services business:
- construction planning business
- construction performance business
- construction supervision business.
However, Law 18/1999 did not stipulate further the general and specialist classification and the scope of business activities of each type of construction business.
New Construction Law:
The New Construction Law regulates 3 types of construction service business:
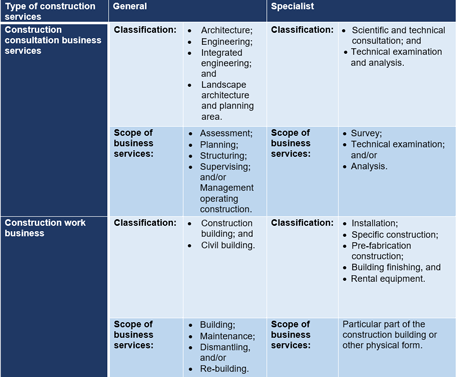
- construction consultation business services
- construction work business
- integrated construction business.
The construction consultation business services and the construction work business are subdivided into general and specialist classifications as described in the table below:
With regard to the integrated construction services, there are 2 types of classification, namely building construction and civil construction. The scope of business services are (i) building plans, and (ii) engineering, procurement, and execution.
Please note that the New Construction Law also requires construction service providers to prioritize domestic production.
2. Foreigners required to establish representative offices or legal entities
The New Construction Law requires foreign construction business entities and foreign individuals to establish either of the following:
3. Additional mandatory clauses stipulated in construction work contract
The New Construction Law stipulates additional mandatory clauses in the construction work contract as follows:
- protection to third parties in the event of damage, accident and/or death;
- guarantee on the risk and liabilities incurred to third parties in the performance of construction work or failure of the buildings; and
- construction work contracts need to be in the Indonesian language.
Where a foreign party is involved however, the contract will need to be both in the Indonesian and English language. In the event of a dispute, the contract which is in the Indonesian language shall prevail as the governing language.
Further regulations on this will be made in the Government Regulation.
4. Expansion of manner in which building supply business can be conducted
The New Construction Law has expanded the way building supply business (usaha penyediaan bangunan) service can be conducted i.e., through cooperation between central government and/or regional government and the business entities and/or community. The provisions related to the contract on building supply shall be further regulated in the presidential regulation.
5. Financing and guarantees
The New Construction Law regulates that:
- The construction service user is responsible for all construction service costs based on the construction work contract, which is evidenced by the ability to pay (i.e. financial capability statement from bank or non-bank institution) and/or commitment upon procurement of construction service product (i.e partnership agreement).
- The construction service provider shall deliver the following guarantees to the construction service user for the purpose of fulfilling requirements for service provider selection:
- bid bond;
- performance bond;
- advance payment guarantee;
- maintenance guarantee; and/or
- appeal objection guarantee.
6. Qualification criteria for construction workers
The New Construction Law classifies the qualification of the construction workers to be (i) operator, (ii) technician or analyst; and (iii) expert. Construction workers must undergo a competency test organised by a certified institution that is registered with the Ministry of Public Works, to obtain a decent remuneration.
7. System information of construction service
The Government of Indonesia is planning to create integrated system information in order to provide an accurate and integrated data and information in conducting construction services. In this respect, the user and provider of construction services are obligated to provide data and information to this system regarding responsibilities, authorities, development and service duties conducted by central and local government in the construction service field.
8. Administrative sanction
The New Construction Law removes the criminal sanction, which was previously regulated in the Law 18/1999, and only imposes administrative sanctions, such as, written warning, administrative fee, temporary suspension of the construction activity, blacklisted, and accreditation suspension and revocation.
9. New chapters
There are several new chapters added or explained in detail in the New Construction Law, which are as follows:
- responsibilities and authorities of central and local Government;
- sustainable business development;
- building failure and specialist appraiser;
- qualification and classification of construction worker, including professional responsibility;
- public participation; and
- dispute settlement mechanism.
If you have any questions or require any additional information, please contact Afriyan Rachmad, Evi Pasaribu, Sianti Candra or the ZICO Law Partner you usually deal with.
This alert is for general information only and is not a substitute for legal advice.